RightBattery.com
Tests and reviews of different batteries to help you find the Right One…
Search
Posts Tagged ‘carbon-zinc’
Common Consumer Batteries and the Names Used
4, Aug 2013
There are multiple battery sizes that are the most commonly used ones, these are the AAA, AA, C, D and 9V batteries that can be either primary (single use) as well as rechargeable. But these batteries also have many other names, some of which are used by different manufacturers and in some countries the other names may be more popular than the typical types mentioned above.
AAA Alkaline Battery – MN2400, LR03, E92, 4203/4003, K3A, AM4, 824, LR03, 24A, R03 (carbon–zinc), 24D (carbon–zinc)
AAA Rechargeable Battery – HR03 (NiMH), MIGNON, MINI-STILO, 4003, E92, K3A, R0, UM4, KR03 (NiCd), ZR03 (NiOOH)
The typical capacity of an AAA size alkaline battery is around 1000-1200 mAh, for Carbon-Zinc batteries the capacity is around 500 mAh and the rechargeable AAA batteries of the NiMH type usually offer abound 800-1000 mAh capacity.
AA Alkaline Battery – MN1500, LR6, E91, 4206/4006, KAA, AM3, 815, LR6, R6 (carbon–zinc), 15D (carbon–zinc)
AA Rechargeable Battery – HR6 (NiMH), MICRO, STILO, 4006, E91, KAA, R6, UM3, KR6 (NiCd), ZR6 (NiOOH)
The typical capacity of an AA size alkaline battery is around 1500-2500 mAh, for Carbon-Zinc batteries the capacity is around 500-800 mAh and the rechargeable AA batteries of the NiMH type usually offer abound 1600-2900 mAh capacity.
C Alkaline Battery – MN1400, LR14, E93, 4014, KC, AM2, 814, LR14, R14 (carbon–zinc), 14D (carbon–zinc)
C Rechargeable Battery – HR14 (NiMH), BABY, MEZZA-TORCIA, 4014, E93, KC, R14, UM2, KR14 (NiCd), ZR14 (NiOOH)
The typical capacity of a C size alkaline battery can be up to about 8000 mAh, for Carbon-Zinc batteries the capacity can be up to about 4000 mAh and the rechargeable C batteries of the NiMH type usually offer abound 4500-6000 mAh capacity. Alternatively there are also special plastic adapters that can be used together with an AA battery to make a C size cell, though the capacity would be lower in this case than what a C size battery would normally provide.
D Alkaline Battery – MN1300, LR20, E95, 4020, KD, AM1, 813, LR20, 13D (carbon-zinc), R20 (carbon-zinc)
D Rechargeable Battery – HR20 (NiMH), HR20, MONO, TORCIA, 4020, E95, KD, R20, UM1, KR20 (Ni-Cd), ZR20 (NiOOH)
The typical capacity of a D size alkaline battery can be up to about 12000 mAh, for Carbon-Zinc batteries the capacity can be up to about 8000 mAh and the rechargeable D batteries of the NiMH type usually offer abound 2000-12000 mAh capacity. Alternatively there are also special plastic adapters that can be used together with an AA battery to make a D size cell, though the capacity would be lower in this case than what a D size battery would normally provide.
9V Alkaline Battery – MN1604, 6LR61, 522, 4022, K9V, 6AM6, A1604, 6LR61, 1604D (carbon‑zinc), 6F22 (carbon-zinc), 1604LC (lithium)
9V Rechargeable Battery – HR9V (NiMH), HR9V, E-BLOCK, TRANSISTOR, 422, 4022, 6F22, K9V, 6HR61, 6KR61 (NiCd), 11604 (NiCd)
The 9V batteries essentially consists of multiple cells to bring up the voltage higher – 6x 1.5V cells for carbon-zinc; 3 cells for Lithium; 6, 7 or 8 cells for NiMH (7.2V, 8.4V or 9.6V) using 1.2V cells. Alkaline batteries can go up to about 500-600 mAh capacity, 400 mAh for the carbon‑zinc, up to about 1200 mAh for lithium (non-rechargeable), 200–300 mAh for NiMH and about 100 mAh for NiCd.
- In: Useful Battery Articles
- Tags: 9V, aa, AAA, alkaline batteries, battery names, C, carbon-zinc, D, lithium, NiCd, nimh, rechargeable batteries

The 1.5V AA Sony Ultra Heavy Duty Carbon Zinc batteries we’ve got for testing here are marked with a code SUM3-NUB4A on their box, they are under warranty until 03-2015. We could not find specifications for these batteries provided by Sony, the only thing Sony does is to say that they are: “Ideal for use in low drain applications such as remote controls, torches, toys, calculators and radios”. And don’t be fooled by the Heavy Duty in the name, with Zinc-carbon batteries this usually means you get the slightly better version and not the the lower capacity ones, however even these are performing worse than standard Alkaline batteries.
Zinc–carbon batteries are the least expensive primary batteries (single use ones) and are intended for low current drain applications. These batteries are getting harder to find as they are mostly being replaced by Alkaline batteries (slightly more expensive and better performing), however you can still find slightly cheaper Carbon Zinc batteries mixed among Alkaline batteries in a store, so you should be careful when choosing based on your needs. For higher drain applications it is advisable to consider Alkaline or even NiMH batteries over Zinc–carbon ones.
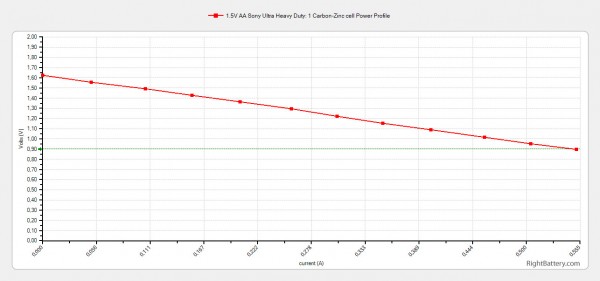
The Power Profile test checks how the battery handles different current loads before it reaches the cutoff voltage, the test starts at 0A and gradually increases with steps of 0.05A each 20 seconds, until it the cutoff voltage of the cell is reached (0.9V in the case of Zinc-carbon cells). In the case of the 1.5V AA Sony Ultra Heavy Duty Carbon Zinc batteries when a current load of 0.55A is applied the battery’s voltage quickly drops to the cutoff value, meaning that the battery is unable to handle such high current loads. As expected the Zinc-Carbon batteries are not able to handle higher current draw as good as Alkaline batteries for example as they are intended for lower current drain applications than Alkaline.
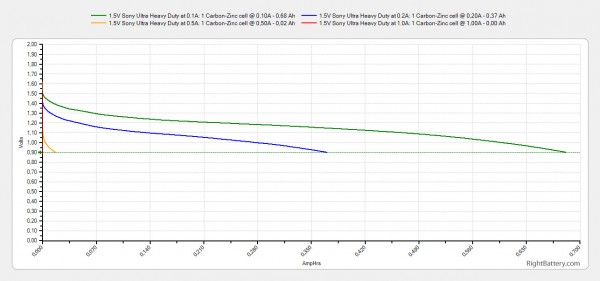
The Open Circuit Voltage (no load voltage) of the 1.5V AA Sony Ultra Heavy Duty Carbon Zinc batteries is 1.62V, though under load it quickly drops to 1.5V or lower depending on the current load of the battery. We are testing all Carbon Zinc as well as Alkaline batteries with a constant current discharge rate of 0.1A, 0.2A, 0.5A and 1A and measuring what capacity they can provide at these levels.
What we got out of the 1.5V AA Sony Ultra Heavy Duty Carbon Zinc in our tests:
– 681 mAh at 0.1A load
– 370 mAh at 0.2A load
– 17 mAh at 0.5A load
– 0 mAh at 1.0A load
– 0.783 Wh at 0.1A load
– 0.398 Wh at 0.2A load
– 0.016 Wh at 0.5A load
– 0 Wh at 1.0A load
As expected from a Zinc-carbon battery the capacity you can get under low current load is decent, but as you increase the load the useable capacity drops quite significantly. So the 1.5V AA Sony Ultra Heavy Duty Carbon Zinc batteries may not be bad as long as you are using them only for the right things – devices with low power requirements.
